Cnr-Irea: terremoto - movimento laterale 16 cm
Nuovi risultati sulle deformazioni del suolo del terremoto di Amatrice ottenuti grazie ai dati dei satelliti SENTINEL-1. L'analisi delle immagini radar acquisite dai satelliti Sentinel-1A e Sentinel-1B del Programma Europeo COPERNICUS ha consentito ad un team di ricercatori dell'Istituto per il rilevamento elettromagnetico dell’ambiente (Irea) di ottenere nuove informazioni riguardanti il campo di deformazione del suolo provocato dal terremoto di Amatrice.
In particolare, combinando le informazioni ottenute dalle immagini acquisite dalle orbite ascendenti e discendenti dei satelliti Sentinel-1, è stato possibile rilevare sia la componente verticale della deformazione del suolo, sia quella nella direzione Est-Ovest. Queste informazioni sono particolarmente importanti per lo studio delle faglie sismogeniche.
Nota stampa ESA:
SENTINEL-1 PROVIDES NEW INSIGHT INTO ITALY’S EARTHQUAKE
29 August 2016
On 24 August, an earthquake struck central Italy, claiming at least 290 lives and causing widespread damage. Satellite images are being used to help emergency aid organisations, while scientists have begun to analyse ground movement.
The Italian peninsula is prone to earthquakes owing to the fault lines created by the separation of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates. The fault line separating these two plates runs below the central Apennine mountains and along Italy’s Adriatic coast.
Under the coordination of the Italian Department of Civil Protection, scientists from Italy’s National Institute for Geophysics and Volcanology and the Institute for Electromagnetic Sensing of the Environment of the National Research Council are studying data from the Sentinel-1 satellite mission and other spaceborne radar missions to map surface deformations caused by the earthquake.
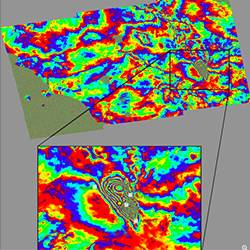 The team found that the main deformation pattern shows subsidence reaching about 20 cm in the Accumoli area, and sideways movement of up to 16 cm.
The team found that the main deformation pattern shows subsidence reaching about 20 cm in the Accumoli area, and sideways movement of up to 16 cm.
The scientists use a technique that allows them to map surface deformations by comparing radar images over the affected area taken before and after the event.
The team has benefited from the availability of both Sentinel-1A and Sentinel-1B scans. The scientists were able to quantify the ground movement in both vertical and east–west directions by combining the radar scans obtained as the satellites flew both south to north and north to south.
Sentinel-1 is not the only satellite providing information on this recent quake: scientists are also relying on data from the Italian space agency’s Cosmo-SkyMed satellites, as well as satellite imagery from other space agencies.
In addition, data from a multitude of Copernicus contributing missions are being used to produce maps through the Copernicus Emergency Management Service for damage assessment.
 Sentinel-1 is a two-satellite mission for Europe’s Copernicus environment monitoring programme, led by the European Commission. The first satellite – Sentinel-1A – was launched in 2014, while its sister Sentinel-1B is still in its commissioning phase following launch just four months ago.
Sentinel-1 is a two-satellite mission for Europe’s Copernicus environment monitoring programme, led by the European Commission. The first satellite – Sentinel-1A – was launched in 2014, while its sister Sentinel-1B is still in its commissioning phase following launch just four months ago.
With its 250 km-wide swatch over land surfaces, Sentinel-1 gives scientists a broad view of the displacement, allowing them to examine the ground displacement caused by this earthquake and develop the scientific knowledge of quakes.
Once Sentinel-1B is operational next month, it will be possible to perform routine scans over critical areas like Italy every six days with the two-satellite constellation.
LINK alla Pagina ESA: http://m.esa.int/Our_Activities/Observing_the_Earth/Copernicus/Sentinel-1/Sentinel-1_provides_new_insight_into_Italy_s_earthquake

